Profundice en la tecnología de NEAR
Este módulo ofrece una inmersión profunda en los aspectos técnicos de Near Protocol. Exploraremos el mecanismo de consenso único de NEAR y comprenderemos cómo contribuye a la escalabilidad y seguridad de la plataforma. El módulo también examinará en detalle las características de escalabilidad y seguridad de Near Protocol, destacando cómo se comparan estas características con otras plataformas blockchain. Además, proporcionaremos un análisis comparativo de Near Protocol con otras blockchains, analizando sus fortalezas y posicionamiento en el ecosistema blockchain más amplio. Este módulo está diseñado para proporcionar una comprensión técnica profunda de la tecnología innovadora de Near Protocol y sus implicaciones para el futuro del desarrollo de blockchain.
Mecanismo de consenso de NEAR
El mecanismo de consenso es un componente crítico de cualquier tecnología blockchain, ya que determina cómo se verifican las transacciones y cómo la red logra un acuerdo. Near Protocol emplea un mecanismo de consenso único conocido como Nightshade, que lo distingue en el panorama blockchain. Nightshade está diseñado para optimizar tanto la velocidad como la seguridad, abordando los desafíos comunes que enfrentaban las tecnologías blockchain anteriores. Este mecanismo permite un alto rendimiento de transacciones, un requisito crucial para la adopción generalizada y el uso práctico de la tecnología blockchain.
Nightshade opera según el principio de fragmentación, que implica dividir la red en múltiples fragmentos que procesan transacciones y almacenan datos de forma independiente. Esta división permite que la red maneje una mayor cantidad de transacciones simultáneamente, lo que aumenta significativamente la capacidad general de la cadena de bloques. Cada fragmento procesa una parte de las transacciones totales y luego los resultados se combinan para formar un estado de cadena de bloques único y unificado. Este proceso es clave para lograr la escalabilidad que busca Near Protocol.
La seguridad del mecanismo de consenso de Nightshade se mantiene mediante una selección aleatoria de validadores para cada fragmento. Los validadores desempeñan un papel crucial en el proceso de consenso, ya que son responsables de procesar transacciones y crear nuevos bloques en la cadena de bloques. El proceso de selección aleatoria garantiza que se minimice el riesgo de ataques maliciosos o colusión, ya que resulta poco práctico para los atacantes predecir qué fragmento necesitarán controlar para influir en la red.
Nightshade también incorpora varios mecanismos para garantizar la coherencia e integridad de los datos en todos los fragmentos. Esto incluye protocolos de comunicación entre fragmentos que permiten que los fragmentos interactúen y validen transacciones que involucran múltiples fragmentos. Estos protocolos están diseñados para ser eficientes y seguros, garantizando que la integridad de la cadena de bloques se mantenga incluso a medida que la red escala.
Hierba mora
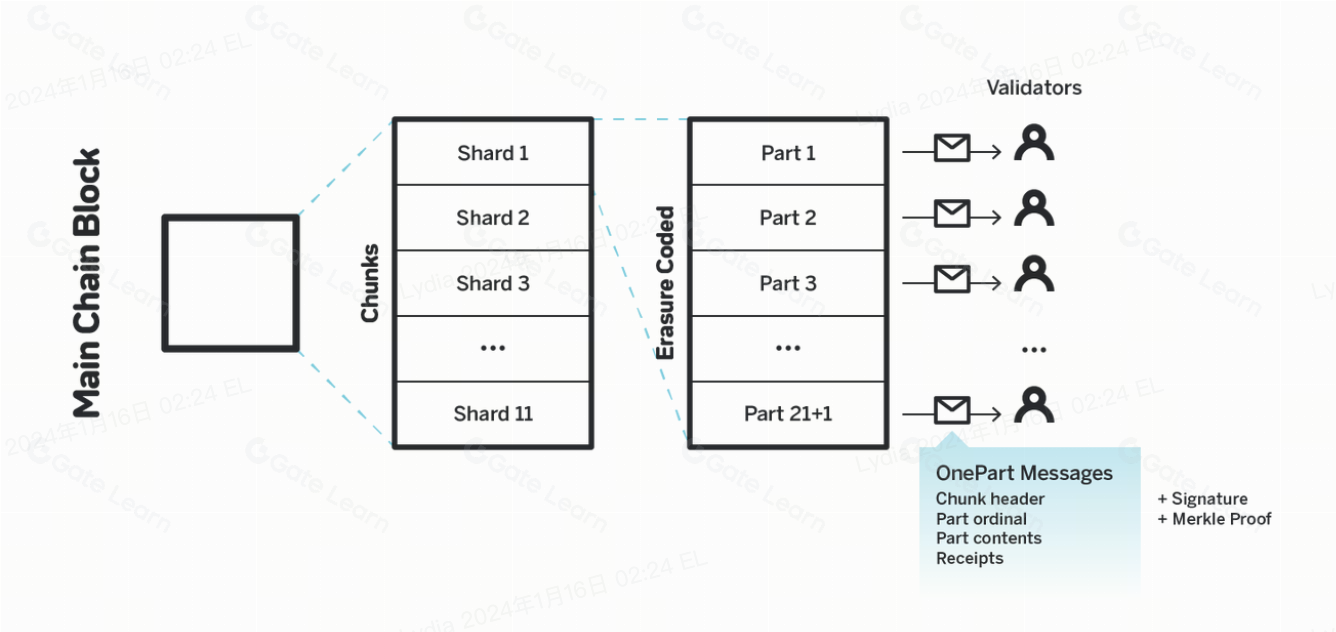
Nightshade está diseñado para abordar los problemas de escalabilidad comúnmente asociados con las redes blockchain mientras mantiene altos niveles de seguridad y descentralización. Nightshade opera dividiendo la cadena de bloques en múltiples fragmentos, y cada fragmento procesa una parte de las transacciones de la red. Este enfoque de fragmentación permite el procesamiento paralelo, lo que aumenta significativamente la capacidad general y la velocidad de la cadena de bloques. En Nightshade, cada fragmento produce una fracción del siguiente bloque, conocido como "fragmento". Luego, estos fragmentos se compilan para formar un bloque completo en la cadena de bloques.
El mecanismo de consenso en Nightshade es único porque combina elementos de los sistemas Prueba de trabajo (PoW) y Prueba de participación (PoS). Los validadores de la red se eligen en función de su participación y son responsables de producir bloques y validar transacciones. Este sistema garantiza que los validadores tengan un interés personal en mantener la integridad y seguridad de la red.
El mecanismo utiliza una versión del protocolo "GHOST" (Greedy Heaviest Observed Subtree) para la producción de bloques, lo que garantiza que los bloques se produzcan de forma rápida y coherente. Este enfoque permite que el protocolo NEAR logre un alto rendimiento de transacciones sin comprometer la seguridad o la descentralización.
Funciones de escalabilidad y seguridad
La escalabilidad es una preocupación primordial en la tecnología blockchain, y Near Protocol aborda esto a través de su diseño innovador. La escalabilidad de la plataforma se atribuye en gran medida a su mecanismo de fragmentación, que permite a la red procesar un gran volumen de transacciones distribuyendo la carga entre múltiples fragmentos. Esto significa que a medida que la red crece y aumenta el número de transacciones, Near Protocol puede escalar en consecuencia sin enfrentar los cuellos de botella que limitan las cadenas de bloques tradicionales. Esta escalabilidad es crucial para la capacidad de la plataforma de admitir una amplia gama de aplicaciones y una base de usuarios en crecimiento.
Además de la escalabilidad, la seguridad es una de las principales prioridades de Near Protocol. La plataforma emplea varias medidas de seguridad para proteger contra amenazas comunes en el espacio blockchain. Esto incluye técnicas criptográficas sólidas para proteger transacciones y datos, así como mecanismos para evitar el doble gasto y otros tipos de fraude. La naturaleza descentralizada de la plataforma mejora aún más su seguridad, ya que elimina puntos únicos de falla y la hace más resistente a los ataques.
Las funciones de seguridad de Near Protocol están diseñadas para ser sólidas y eficientes. La plataforma utiliza algoritmos criptográficos livianos que brindan un alto nivel de seguridad sin afectar significativamente el rendimiento. Este equilibrio entre seguridad y eficiencia es fundamental para mantener el rendimiento de la plataforma incluso a medida que escala.
La plataforma también incluye funciones para mejorar la seguridad del usuario. Esto incluye opciones de recuperación de cuenta fáciles de usar y la capacidad de configurar la autenticación multifactor. Estas características facilitan a los usuarios la protección de sus cuentas y activos, contribuyendo a la seguridad general del ecosistema.
Comparación con otras cadenas de bloques
Al comparar Near Protocol con otras tecnologías blockchain, se hacen evidentes varias diferencias clave. Uno de los más notables es su enfoque de la escalabilidad. Si bien muchas cadenas de bloques luchan con problemas de escalabilidad, el mecanismo de fragmentación de Near Protocol le permite procesar un gran volumen de transacciones de manera eficiente. Esto lo distingue de plataformas como Bitcoin y Ethereum, que han enfrentado desafíos de escalamiento manteniendo la seguridad y la descentralización.
Otro punto de comparación es la velocidad y el costo de las transacciones. El mecanismo de consenso de Near Protocol le permite procesar transacciones más rápido y a un costo menor que muchas otras cadenas de bloques. Esto es particularmente importante para aplicaciones que requieren alto rendimiento y bajas tarifas de transacción, como microtransacciones y aplicaciones de finanzas descentralizadas (DeFi).
En términos de experiencia de desarrollador, Near Protocol ofrece un entorno más accesible y fácil de usar en comparación con otras plataformas blockchain. Su compatibilidad con lenguajes de programación comunes y herramientas de desarrollo integrales facilita a los desarrolladores la creación e implementación de aplicaciones. Esto contrasta con las plataformas que tienen una curva de aprendizaje más pronunciada o requieren conocimientos especializados de lenguajes de programación específicos de blockchain.
El modelo de gobernanza de Near Protocol también es un factor distintivo. La gobernanza impulsada por la comunidad de Near permite un enfoque más democrático y participativo para la toma de decisiones. Esto contrasta con otras cadenas de bloques donde la gobernanza es más centralizada o menos transparente.
Reflejos
- El exclusivo mecanismo de consenso Nightshade de Near Protocol optimiza la velocidad y la seguridad, abordando los desafíos de escalabilidad comunes en la tecnología blockchain.
- Nightshade emplea fragmentación, dividiendo la red en múltiples fragmentos para el procesamiento de transacciones en paralelo, lo que aumenta significativamente el rendimiento.
- La seguridad en Nightshade se ve reforzada mediante la selección aleatoria de validadores para cada fragmento, lo que minimiza los riesgos de ataques y garantiza la integridad de los datos.
- La escalabilidad de Near Protocol se logra sin comprometer la seguridad, utilizando técnicas criptográficas y evitando el doble gasto y el fraude.
- En comparación con otras cadenas de bloques, Near Protocol sobresale en escalabilidad y eficiencia, manejando un mayor volumen de transacciones de manera más efectiva.
- Near ofrece un entorno más accesible para los desarrolladores, con soporte para lenguajes de programación comunes y herramientas de desarrollo fáciles de usar.
- El enfoque de Near Protocol en la gobernanza impulsada por la comunidad y la experiencia del usuario, incluidas características como nombres de cuentas legibles por humanos, lo distingue de otras plataformas blockchain.





