暗号資産の自動投資ガイド
自動投資は、一定額の資金を使い、定期的に決められた投資資産を購入することで、平均コストを目指しつつ価格変動やリスクの軽減を図る、受動的な投資戦略です。
序文
現代社会では、投資や資産運用が一般化しているが、多くの方にとっては馴染みがなく、難解に感じられることも少なくない。特に売買のタイミングは、暗号資産市場のような価格変動の激しい環境下で、常に投資家やトレーダーの悩みの種である。明確な戦略がなければ、こうした変動市場で損失を被るリスクが高まる。
この課題に対し、トレーダーは売買の機会を見極めるため、多様な投資戦略を選択する。その一つが自動積立投資であり、決められた金額で定期的に資産ポートフォリオを購入することで、パッシブな資産運用を実現する。
本レポートでは、自動積立投資戦略について、基本的な概念や原理、主要な用語、運用原則、メリット・デメリットまで包括的に解説する。自動積立投資戦略の理解と応用を深め、今後の投資・資産運用の基盤構築に資する。
自動積立投資とは?
自動積立投資は、同じ金額で定期的に特定の投資資産を購入する投資戦略である。分割投資によって価格変動やリスクを分散し、積立回数が増えるほど保有資産の平均取得コストがならされる。初出時のみ「ドルコスト平均法(Dollar Cost Averaging、DCA)」とも呼ばれる。
この戦略では、資産価格が上昇した場合は購入数量を減らして高値掴みを避け、逆に価格が下落した場合は購入数量を増やして取得コストを下げ、価格回復時の利益獲得を図る。自動積立投資は取得コストの平均化と高値掴みリスクの軽減、有利なタイミングでの参入確率の向上に寄与する。
自動積立投資はパッシブな投資戦略である。アクティブな投資戦略に比べて容易で、リスクが相対的に低く、長期的に安定したリターンが得られる。価格の動きを細かく監視する必要がなく、計画通りに投資を実行できるため、初心者にも向いている。
自動積立投資戦略の多様な形態
ドルコスト平均法(DCA)
DCAは定期積立投資戦略の原型であり、投資頻度と一回あたりの投資金額という2つの要素によって決まる。投資頻度は投資期間中の購入回数を、一回あたりの投資金額はポジションの取得コストに影響する。資産価格の上下を問わず、事前に定めたスケジュールで「バイ&ホールド(HODL)」を実行する。長期で見れば、購入価格は投資期間の資産平均価格に近づく。
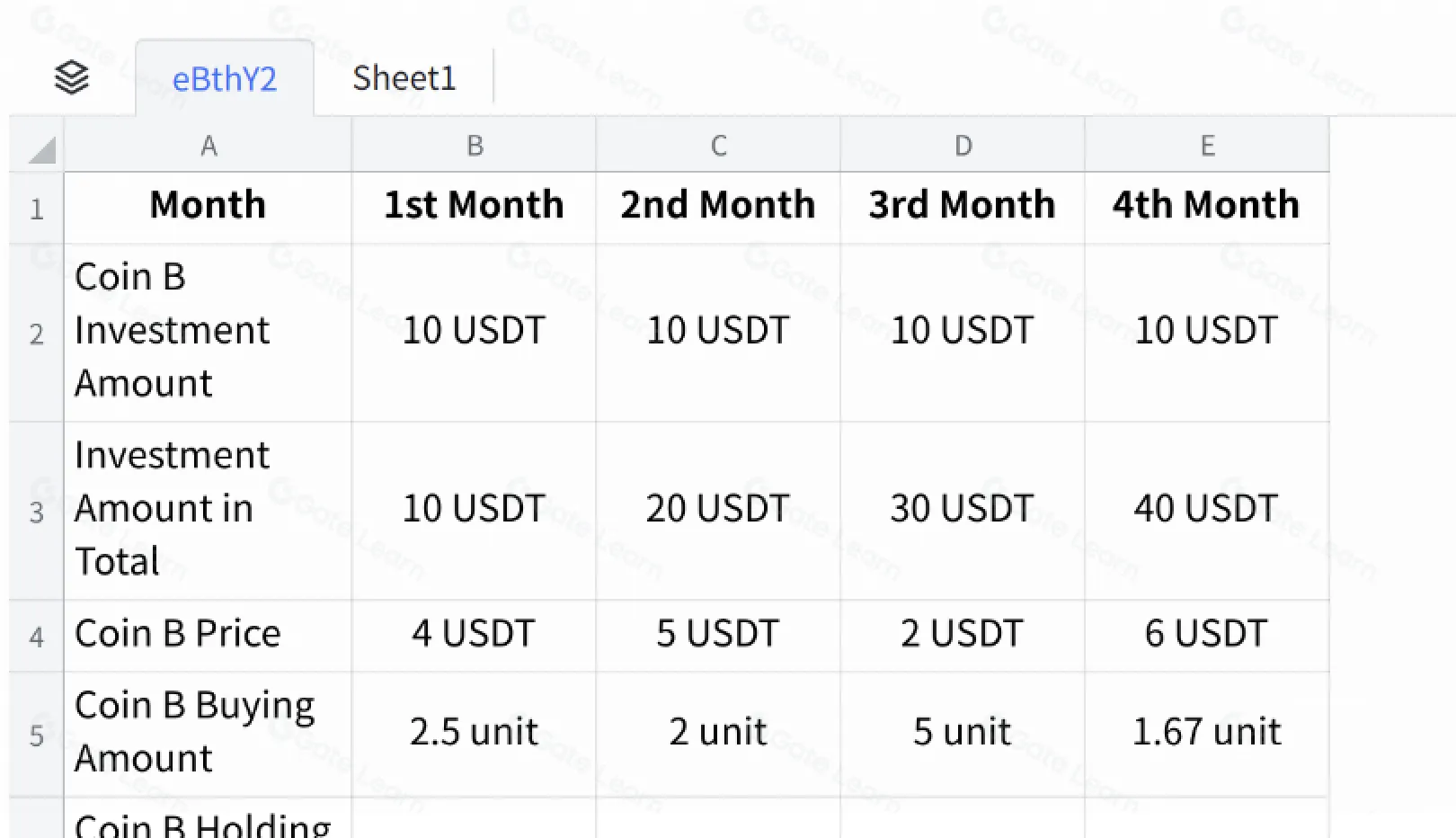
下記の表のように、毎月10 USDTでコインBを購入するDCAの場合、価格上昇時には購入量が減り、価格下落時には購入量が増える。価格が下落した期間は損失も出るが、ポジションが増えることで価格上昇時に高いリターンを得られる。
バリューアベレージング
バリューアベレージングは、自動積立投資に近い戦略であり、DCAとは異なり資産価格の変動に応じて購入金額を調整する。各期間ごとに目標投資額を設定し、前期間の資産価格と目標額との差分に基づいて当期間の投資額を調整し、均等な投資分散を図る。
資産価格が下落すれば投資額を増やし、価格が上昇すれば投資額を減らす。過剰なポジション取得を避けるため、各投資期間前に調整額を慎重に計算する必要がある。
例えば、毎月BTCポジションを100 USDT分増やす目標を設定し、前月のビットコイン価格上昇で保有BTC価値が50 USDT増加した場合、今月は追加で50 USDT分だけ購入すれば目標を達成できる。逆に翌月ビットコイン価格が50 USDT分下落した場合は、150 USDT分を購入して目標を達成する。
ローリングインベストメント
ローリングインベストメントは、資産価格の変動を踏まえて定期的・自動的に投資を行う戦略であり、バリューアベレージングより柔軟性がある。価格下落だけでなく価格上昇時にも追加入金が可能で、市場動向やトレンド形成を捉えるために市場状況の綿密な監視が求められる。
トークン価格が下落した場合は投資額を減らし、リスクを回避する。初回投資額が100ドルで次回価格が10%下落した場合、投資額は90ドルに減額する。さらに下落した場合は追加減額し、コスト平均化と過剰ポジション回避を両立する。
逆に、トークン価格が110ドルに上昇し、さらに上昇する場合は次回投資額も110ドルに増やす。ローリングインベストメントは、トレンド市場での大きな利益獲得を目指す戦略である。
コインベース型自動積立投資
コインベース型自動積立投資は、特定の暗号資産(例:ビットコイン)を使って他の暗号資産(例:ETHやUSDT)を購入する逆DCA戦略である。投資家は決まった間隔で一定量の暗号資産を他通貨に交換する。
例えば、ビットコインマイナーがBTCで定期収入を得ていて、ETH価格の上昇を狙う場合、毎週0.01 BTCでETHを購入することでコインベース型自動積立投資戦略を構築できる。BTC価格の上下に関わらず、同じ量のBTCで他通貨を一貫して購入する。
定期的にBTCを売却して他暗号資産のポジションを構築することで、他通貨の価格が下落した場合は有利な平均取得価格で購入でき、価格が上昇した際には売却してBTCベースのリターンを得る。
自動積立投資の原則
自動積立投資はパッシブな投資手法だが、必ずしも成功が保証されるわけではない。参入障壁を下げてリスクを緩和することが主な役割であり、実際の利益獲得の鍵は有望な投資対象の選定にある。
下落を続ける資産は平均取得コストが下がり続けるのみで、損益分岐点を超えることはできない。持続的成長が見込める高品質資産こそ長期保有に適している。パッシブな自動積立投資を継続することで、時間的な優位性を得ることができる。
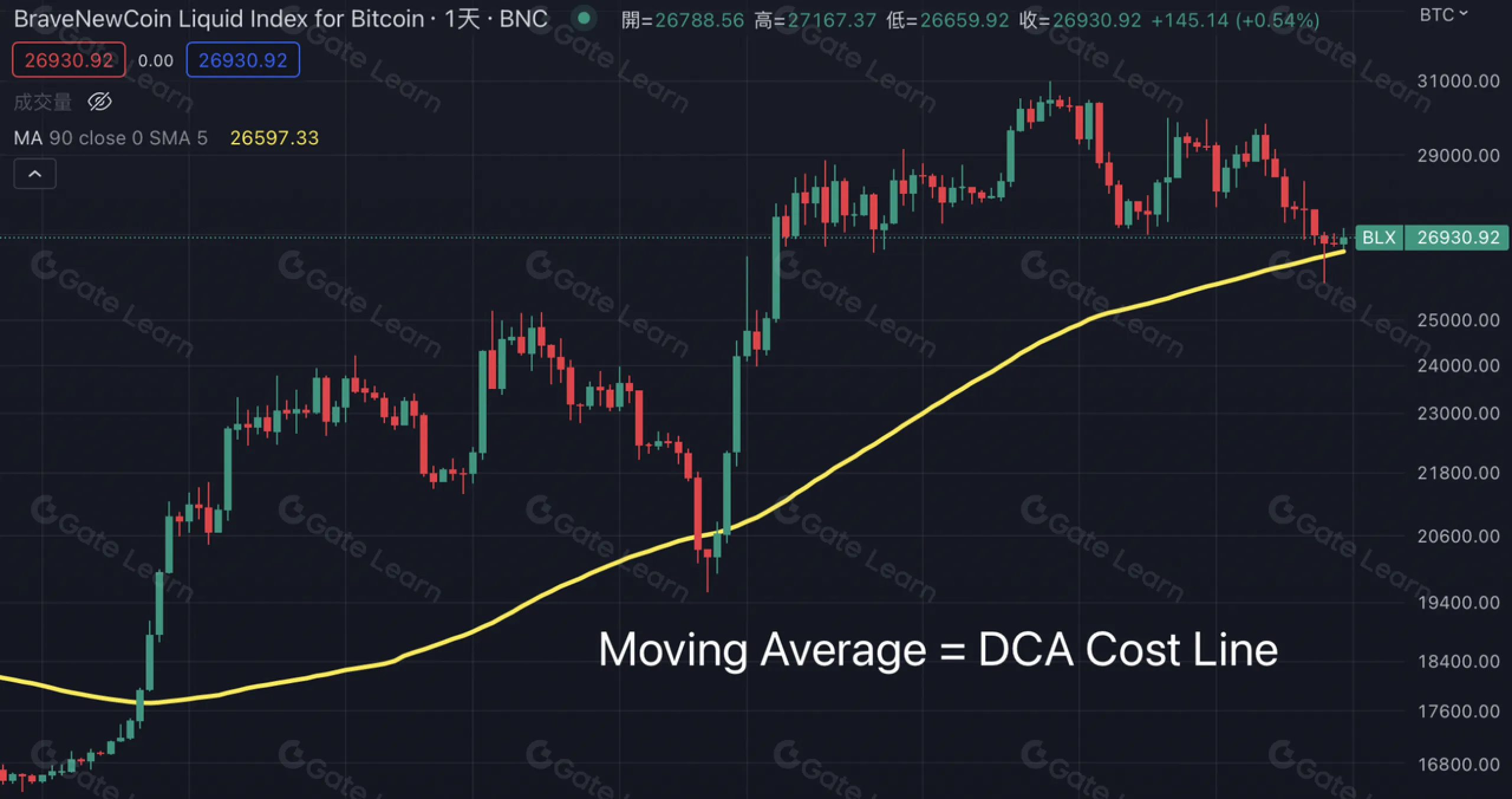
十分な投資期間を設ければ、自動積立投資戦略のコストラインは基礎資産の移動平均線に近づく。例えば、特定の暗号資産に30日連続で投資した場合、平均取得コストはその資産の30日移動平均線に近づく。
市場価格が移動平均線を上回れば、自動積立投資戦略は利益を生んでいる。その際は投資継続や利益確定を検討できる。反対に、市場価格が移動平均線を下回れば損失状態であり、市場反転まで自動積立投資を継続することが望ましい。
移動平均線はDCAコストラインの目安となるため、戦略の実行や終了判断の参考指標として活用できる。
自動積立投資の開始タイミング
自動積立投資戦略は厳密なタイミング調整を必要としない。長期的に価格上昇が見込める高品質資産であれば、いつでも購入の好機となる。そのため、タイミングよりも市場での優良銘柄選定が重要となる。ただし、戦略の収益性は取得コストに依存するため、ファンダメンタル分析やテクニカル分析で比較的安値を見極めることで収益性を高めることができる。
暗号資産市場の価格推移を見ると、主要銘柄の多くはビットコインと高い相関性を持つ。ビットコインは約4年ごとに3回の半減期を経ており、それぞれの半減期後1年程度で高値となり、次回半減期の前年には安値となる傾向がある。暗号資産市場の周期性を活用すれば、投資家は長期的な自動積立投資戦略を効果的に実施できる。
自動積立投資戦略のメリット・デメリット
自動積立投資戦略のメリット:
- 市場変動の平準化
異なるタイミングで分割投資を行うことで、一括投資による不利な状況や市場環境の偏りを回避し、投資コストを平準化できる。 - リスク分散
大きな金額を一度に投資すると高値掴みや急落のリスクがあるが、少額分割投資なら参入タイミングによる取得コストへの影響が小さく、一度の投資による大きな損失を回避できる。 - 簡単な戦略運用
事前に計画的な資金配分が可能であり、都度の資金調達の手間やリスクを避けられる。複雑なタイミング判断が不要で、初心者でも始めやすい戦略である。 - 良好な投資習慣の醸成
長期的かつ継続的な投資により、習慣形成や市場理解力の向上に寄与する。
自動積立投資のデメリット:
- 優良資産への限定
市場リスクや資産パフォーマンスの低下を完全に回避できないため、市場回復を受動的に待つことになる。投資対象の厳選が不可欠である。 - 機会損失
資金が自動積立投資に拘束されることで、他の投資機会を逃す可能性がある。資金回転率の低下が資産運用効果に影響を及ぼすこともある。 - 長期的な希釈効果
積立回数が増えるにつれてリスク分散効果が徐々に薄れ、各回の投資額が総投資額に対する比率として減少するため、リスク分散が十分に機能しなくなる。
まとめ
本レポートでは、取得コストの平均化と価格変動リスクの緩和を目的とした自動積立投資の基本概念を解説した。自動積立投資はパッシブな投資戦略であり、伝統的金融分野でも広く使われている。優良資産を長期にわたり継続して購入・保有することで、安定したリターンが期待できる。
ドルコスト平均法以外にも、バリューアベレージングやローリングインベストメントなど様々な形態が存在し、比較的リスクが低く、安定した長期リターンが得られ、良好な投資習慣の形成にも寄与する。次回はGate.comプラットフォームでの自動積立投資の実践方法について解説する。
ポイント
自動積立投資は、同じ金額で定期的に資産を購入し、取得コストの平均化と価格変動リスクの緩和を図るパッシブな投資戦略である。
使いやすさ、低リスク、安定した長期リターンを特徴とし、初心者にも適している。
戦略にはドルコスト平均法(DCA)、バリューアベレージング、ローリングインベストメントなど様々な形態がある。
メリットは取得コストの平準化、リスク分散、簡単な運用、良好な投資習慣の形成である。
デメリットは短期的な利益機会の逸失、優良資産への限定、長期的な希釈効果である。
関連記事





