الأسس الفنية للقاعدة
مقدمة الوحدة: يتناول الوحدة الجوانب التقنية لـ Base، بما في ذلك تكنولوجيا البلوكشين الخاصة بها، والميزات الرئيسية، والجوانب التقنية. كما يناقش كيفية عمل Base ضمن نظام الإيثيريوم وتداعياته على القدرة على التوسع والكفاءة.
فهم تكنولوجيا البلوكشين في سياق القاعدة
يعمل Base كحلا للطبقة 2 (L2) على شبكة Ethereum، مستفيداً من تقنية البلوكشين لتعزيز التوسع، الأمان، وكفاءة التكلفة. إنه يستخدم آلة الحساب الظاهرية (EVM) للتوافق، مما يسمح بنشر سلس للتطبيقات والأصول الحالية على شبكة Ethereum. تم تصميم تكامل المنصة مع تقنية البلوكشين لدعم استقطاب قاعدة مستخدمين جديدة ضخمة لنظام البلوكشين.
تعتمد التقنية التي تقف وراء القاعدة على مبادئ اللامركزية والتطوير مفتوح المصدر، وهي سمة من سمات تقنية البلوكشين. يضمن هذا النهج الشفافية والأمان والابتكار الذي يقوده المجتمع داخل النظام الأساسي. كما يمكن لاستخدام تقنية البلوكشين أيضًا للنظام الأساسي توفير بيئة خالية من الثقة حيث يتم تنفيذ المعاملات والعقود دون الحاجة إلى وسطاء.
تم تصميم البنية التحتية لسلسلة كتل Base للتعامل مع حجوم عالية من المعاملات برسوم أقل مقارنة بشبكة Ethereum الرئيسية. يتم تحقيق ذلك من خلال حلول التوسيع المبتكرة مثل rollups، التي تقوم بتجميع عدة معاملات في واحدة واحدة، مما يقلل بشكل كبير من العبء على الشبكة ويقلل من تكاليف المعاملات.
التزام المنصة بتكنولوجيا البلوكشين يمتد إلى خططها للتمزيق التدريجي. تهدف Base إلى التطور لتصبح منصة متمركزة بالكامل، تجسد أساسيات تكنولوجيا البلوكشين من خلال تعزيز اقتصاد رمزي عالمي مفتوح يمكن الوصول إليه من قبل الجميع.
الميزات الرئيسية والتقنيات الأساسية للقاعدة
يتميز Base ببيئته ذات التكلفة المنخفضة والتي تسهل عمل المطورين، مما يجعله منصة جذابة للمطورين. تقدم المنصة بيئة متوافقة مع EVM، مما يضمن أن الأدوات والشيفرات والبنية التحتية الحالية في Ethereum تعمل بسلاسة على Base.
تتمثل إحدى الميزات التقنية الرئيسية ل Base في استخدامها لتقنية التراكم. تلعب عمليات التجميع دورا مهما في تعزيز قابلية تطوير النظام الأساسي من خلال تجميع معاملات متعددة في معاملة واحدة ، وبالتالي تقليل الحمل على الشبكة وخفض رسوم المعاملات.
تقدم Base أيضًا ميزات مبتكرة مثل التجريف الحسابي (ERC4337) وواجهات برمجة التطبيقات للمطورين للمعاملات بدون رسوم. تسهل هذه الميزات تجربة المستخدم وتقلل الحواجز أمام دخول المستخدمين والمطورين الجدد في مجال التقنية اللامركزية.
يتم بناء المنصة على Optimism’s open-source OP Stack، وهو تكنولوجيا أساسية تضمن أمان Base وقابليتها للتوسع وقابليتها للتشغيل مع سلاسل أخرى. توضع هذه الأساسية التقنية Base كمنصة قوية لتطبيقات اللامركزية.
تجريد الحساب (ERC4337)
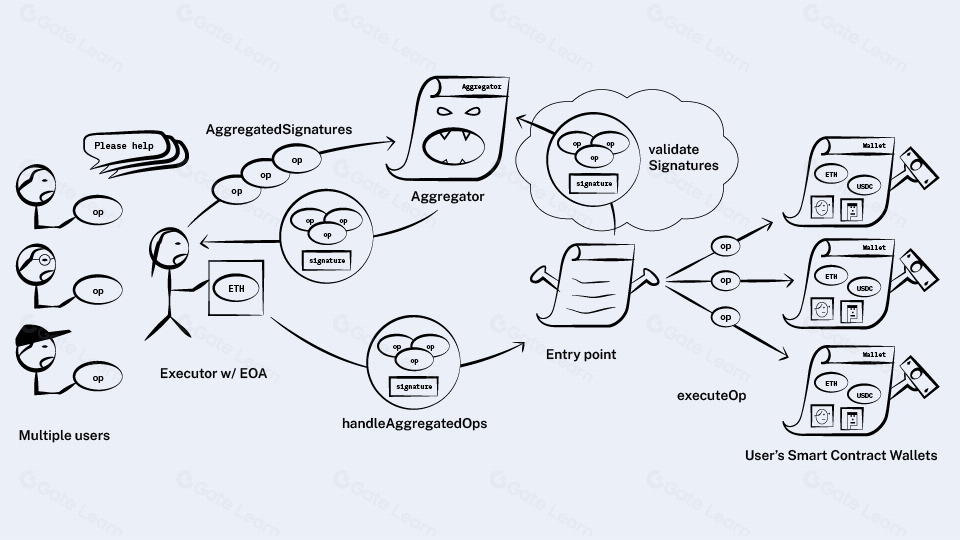
تقسيم حسابات إثيريوم تقليديًا إلى حسابات مملوكة خارجيًا (EOAs) وحسابات عقود، مع الأولى تتطلب مفاتيح خاصة لتوقيع المعاملات. يقترح ERC4337 نموذج حساب موحد حيث تكون حسابات المستخدمين عقودًا ذكية، مما يتيح تفاعلات أكثر تعقيدًا وأمانًا دون تغيير بروتوكول إثيريوم.
يتيح هذا النهج تنفيذ المعاملات بمزيد من المرونة. يمكن للمستخدمين تفويض توقيع المعاملات على Gate.com للكيانات الأخرى، مما يتيح سيناريوهات مثل استعادة الحساب والمدفوعات التلقائية دون المساس بالأمان. هذه المرونة مفيدة بشكل خاص في تطبيقات التمويل اللامركزي (DeFi) على Base، حيث يمكن أن يكون إدارة المعاملات والتفاعلات معقدة.
لم يعد المستخدمون بحاجة إلى إدارة nonce أو القلق بشأن أسعار الغاز ، حيث يمكن التعامل مع هذه الجوانب من خلال عقد الحساب نفسه. يمكن أن يؤدي هذا التبسيط إلى اعتماد أوسع ل Base وتطبيقاتها من خلال جعل تفاعلات blockchain أكثر سهولة للمستخدمين غير التقنيين.
من خلال السماح للحسابات بأن تكون عقود ذكية، يمكن للمستخدمين تنفيذ سياسات أمان مخصصة، مثل متطلبات التوقيع المتعدد أو حدود السحب. هذا المستوى من التحكم هو تحسين كبير على حسابات التشغيل النهائي التقليدية، مما يوفر للمستخدمين أدوات قوية لتأمين أصولهم على Base.
التراص الأساسي للمكدس

من خلال استغلال النسخ المتفائلة، تسهل البنود الأساسية المعاملات الأسرع ورسوم الغاز المنخفضة. تجمع هذه التقنية بين عدة معاملات في كتلة واحدة، والتي يتم تنفيذها بعد ذلك على شبكة إيثيريوم الرئيسية. النتيجة هي تقليل كبير في بصمة المعاملة الفردية، مما يسمح للبنود الأساسية بمعالجة نشاط المستخدمين المتزايد دون إكتظاظ الشبكة.
تستخدم التكنولوجيا دلائل الاحتيال لضمان سلامة المعاملات داخل ال rollup. إذا تم اكتشاف معاملة احتيالية، يمكن تحدي ال rollup وإلغاؤها، مما يحمي أصول المستخدمين. يحافظ هذا الآلية الأمنية على طبيعة الثقة للمعاملات على البلوكشين بينما يعمل ضمن البيئة القابلة للتوسيع التي يوفرها OP Stacks.
تم تصميم التكنولوجيا لتكون متوافقة مع البنية التحتية الحالية ل Ethereum ، مما يسهل على المطورين بناء ونشر التطبيقات اللامركزية (dApps) على Base. يعمل هذا التوافق على توسيع نطاق وصول Base داخل نظام Ethereum البيئي ، مما يسمح بتفاعلات سلسة بين مختلف المنصات والتطبيقات.
تتم تعزيز تجربة المطور من خلال أوبي ستاكس من خلال تبسيط عمليات المعاملات وتقليل التكاليف. يمكن للمطورين إنشاء تطبيقات لامركبة أكثر تعقيدًا دون أن يكونوا مقيدين برسوم الغاز أو ازدحام الشبكة. يشجع هذا على الابتكار وتطوير ميزات وخدمات جديدة على بيس، مما يسهم في نمو وتنوع المنصة.
كيف تختلف القاعدة عن العملات المشفرة الأخرى
تتميز Base عن العملات المشفرة الأخرى من خلال تركيزها على التوسع وسهولة الاستخدام للمطورين. على عكس سلاسل الكتلة التقليدية من الطبقة 1، يعمل Base كحلا Ethereum L2، مما يعالج مباشرة التحديات المتعلقة بالتوسع التي تواجه شبكة Ethereum الرئيسية من خلال تقديم رسوم معاملات أقل وإنتاجية أعلى.
على عكس العديد من منصات البلوكشين، لا يمتلك Base عملة شبكة خاصة به، وهذا خيار متعمد للتركيز على البنية التحتية والفائدة بدلاً من اقتصاديات العملات المشفرة.
إن تكامل المنصة مع Coinbase واستخدامها ل OP Stack من Optimism يميز Base عن العملات المشفرة الأخرى. توفر هذه الشراكات والخيارات التقنية ل Base نظاما بيئيا فريدا يدعم التكامل السلس للتطبيقات ، والأمان المعزز ، ومسارا واضحا نحو اللامركزية ، مما يميزها في مشهد blockchain المزدحم.
يبرز
- Base هو حلاً من الطبقة 2 على إيثيريوم يعزز القابلية للتوسع والأمان وكفاءة التكلفة من خلال تكنولوجيا سلسلة الكتل والتوافق مع الجهاز الظاهري لإيثيريوم (EVM).
- إنها تستخدم تكنولوجيا الRollup لتجميع معاملات Gate.com، مما يقلل من الحمل على الشبكة ورسوم المعاملات، وتدعم النشر السلس لتطبيقات Ethereum.
- تقدم Base ميزات مثل التجريف الحسابي (ERC4337) وواجهات برمجة التطبيقات للمعاملات بدون غاز، بهدف تبسيط مشاركة المستخدم والمطور.
- تم بناء المنصة على OP Stack الخاص بـ Optimism، مما يضمن الأمان القوي، والقابلية للتوسع، والتوافق ضمن نظام البلوكشين.
- توفير التكامل مع كوينبيس يوفر للقاعدة مداخل نقدية سلسة، ويوفر الوصول إلى قاعدة أصول واسعة، ويسهل التكامل مع التطبيقات اللامركزية، مما يعزز من قابلية الاستخدام والوصول.
- تركز Base على التوسع القابل للتوسيع وسهولة الاستخدام من قبل المطورين والشراكات الاستراتيجية تميزها عن العملات المشفرة الأخرى، مما يضعها كلاعب رئيسي في التعامل مع Ethereum’s





